背景
MySQL版本:5.7.18
问题
假设字段category无索引且有重复值,order by category 和limit组合使用的结果会和预期不符。
场景复现
表结构(复现问题,两个字段足够了~)
CREATE TABLE `ratings` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`category` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=11 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_general_ci;对所有数据按category字段排序: select * from ratings order by category;
| id | category |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 |
| 10 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 6 | 2 |
| 9 | 2 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 7 | 3 |
| 8 | 3 |
当我们想分页展示前5条时使用select * from ratings order by category limit 5;
期望得到的ID顺序是1 5 10 3 4。
但实际结果如下:
| id | category |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 10 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 |
可能有同学遇到过这个问题,百度或谷歌一下解决了,你有没有想过,你查到的办法是最优解吗?别人是怎么得出这个办法的?MySQL 为什么会这样做,跟版本有关吗?
先抛结论:
- 最优解是后面再加个列值唯一的排序字段,如:
order by category,id - MySQL 为什么这样做?答案是为了快!(
MySQL 5.6及其之后才有此优化) - 次优解是对
order by后面的category加索引(为什么是次优解?看完本文你将会有答案)
寻找最优解
MySQL 文档 8.2.1.19 LIMIT Query Optimization 中对此场景有如下描述:
If multiple rows have identical values in the
ORDER BYcolumns, the server is free to return those rows in any order, and may do so differently depending on the overall execution plan. In other words, the sort order of those rows is nondeterministic with respect to the nonordered columns.One factor that affects the execution plan is
LIMIT, so anORDER BYquery with and withoutLIMITmay return rows in different orders.
总结来说就是:当 ORDER BY 列的字段值存在重复,那么这条 ORDER BY 语句返回的数据顺序会因为LIMIT的存在而变得不一样。
这是 MySQL 默认对该场景做的优化,如果你需要保证加不加 LIMIT 顺序都要一致,官方也给出了办法:
If it is important to ensure the same row order with and without
LIMIT, include additional columns in theORDER BYclause to make the order deterministic.
就是在ORDER BY后面再多加一个排序字段(比如 ID 字段)。
以上描述最早出现在MySQL 5.6文档中,从这个版本开始,引入了这个针对ORDER BY LIMIT的优化。
好了, 针对文中的场景,我们只需要select * from ratings order by category,id;即可解决。
那么问题来了,MySQL 为什么要做这么一个看似是 Bug 的优化?
MySQL 的 ORDER BY 逻辑
ORDER BY 就是排序。
执行一下explain select * from ratings order by category limit 5;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: ratings
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 10
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using filesort
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)可以看到 Extra: Using filesort 表示需要排序。
正常情况下, MySQL 会有内存排序和外部排序两种:
如果待排序的数据量小于sort buffer size,排序就在内存中完成(快速排序)
如果待排序的数据量大于sort buffer size,就使用临时文件进行外部排序(归并排序)
很明显,这两种排序都是对所有结果全部排序,讲道理,不管有没有LIMIT,都是从排完序的结果中按顺序取需要的条数,有没有LIMIT是不会影响返回的结果顺序的。
但是,MySQL 5.6 版本针对 ORDER BY LIMIT做了个小优化(排序字段无索引,且列值不唯一时):优化器在遇到 ORDER BY LIMIT语句的时候,使用了priority queue。
filesort.cc 中有如下伪代码描述该优化:
while (get_next_sortkey())
{
if (using priority queue)
push sort key into queue
else
{
try to put sort key into buffer;
if (no free space in sort buffer)
{
do {
allocate new, larger buffer;
retry putting sort key into buffer;
} until (record fits or no space for new buffer)
if (no space for new buffer)
{
sort record pointers (all buffers);
dump sorted sequence to 'tempfile';
dump Merge_chunk describing sequence location into 'chunk_file';
}
}
if (key was packed)
tell sort buffer the actual number of bytes used;
}
}
if (buffer has some elements && dumped at least once)
sort-dump-dump as above;
else
don't sort, leave sort buffer to be sorted by caller.并在 WL#1393: Optimizing filesort with small limit 中阐述了该优化逻辑:
Many web customers have to do
"SELECT ... ORDER BY non_index_column LIMIT X",
When X * is smaller than sort_buff_size we can use
the following algoritm to speed up the sort:
- Create a queue to hold 'limit' keys.
- Scan through the table and store the first (last if DESC) keys in the queue
- Return values from queue
This is much faster than the current algoritm that works as:该 WorkLog 中记录了优化后的效果:10 to 20 times faster than a quicksort(感兴趣的同学可以去阅读原文)。
所以,就是为了快!
MySQL 认为这种场景就是求 TOP N 的问题,使用 priority queue 就能解决。
priority queue(优先级队列)
priority queue 其实就是堆,Java 中有java.util.PriorityQueue类,其本质就是 堆 这种数据结构。
简单解释一下什么是堆:
堆是一个完全二叉树;
堆中每一个节点的值都必须大于等于(大顶堆)或小于等于(小顶堆)其子树中每个节点的值。
如果 MySQL 使用归并或快排,需要把所有数据都排好序,再取LIMIT 的前几条,剩余已排序的数据就白白浪费了。
而采用 priority queue 可以根据 LIMIT的条数维护一个堆,只需要把所有数据在这个堆里过一遍就能得到结果。
使用如下语句可以验证 MySQL 使用了 priority queue:
SET optimizer_trace='enabled=on';
select * from ratings order by category limit 5;
SELECT * FROM `information_schema`.`OPTIMIZER_TRACE`\G; "filesort_priority_queue_optimization": {
"limit": 5,
"chosen": true
},可以看到 filesort_priority_queue_optimization.chosen = true
下面用流程图还原一下 priority queue 的执行逻辑(以LIMIT 5为例):
友情提示:图中的小顶堆以 category 值的大小排序
-
取前五条数据构成一个小顶堆:
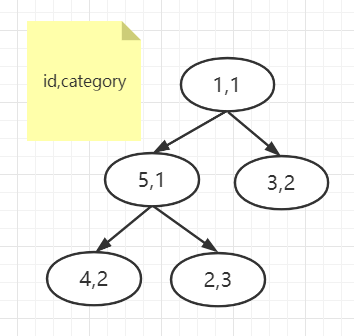
-
取下一行数据(6,2),发现 2 小于当前堆中最大的
category3,于是把(2,3)从堆中删掉,把(6,2) 入堆:
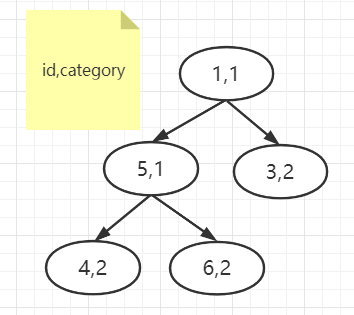
-
重复步骤 2,直至符合查询条件的数据都经历过比较入堆,最终堆中数据如图:
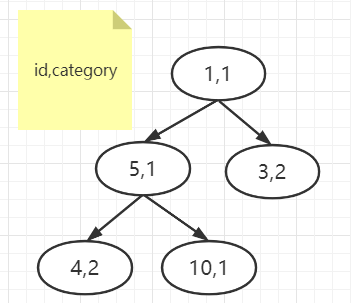
以上就是通过 priority queue 找到 最小的 5 行 category 数据的执行过程。
最后我们将其出堆即可得到结果,每次出堆最小元素后将最后一个元素放入堆顶,按照小顶堆重新堆化,过程如图:
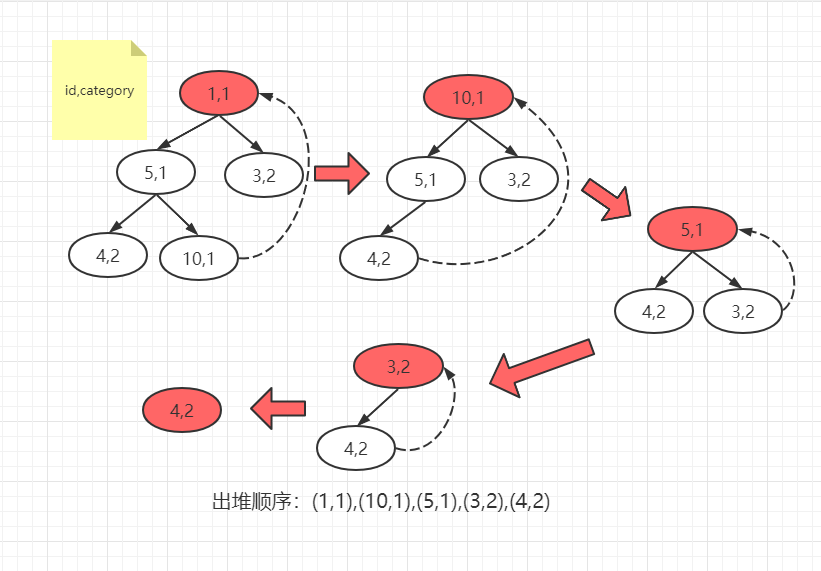
可以看到,这个结果和select * from ratings order by category limit 5;的输出一致
加索引为什么是次优解
显然,按照ORDER BY的逻辑,直接对排序字段加索引也可以省去内存排序步骤,从而解决这个问题。
但索引也不是银弹,多出来的category索引会增加表的维护成本,如果没有明显的业务需要,单纯为了绕过这个priority queue的优化而加索引,有点得不偿失。
尤其是当表数据量非常大的时候,索引的体量会很可观。而且,针对文中场景,category作为分类字段,重复率会比较高,即使有按分类查询的业务 SQL ,MySQL也不一定会选取这条索引。
综上,针对本场景,个人认为order by category,id才是该问题的最优解。